Basic in Windows
Links
Download the docker k8s from: https://docs.docker.com/desktop/vm-vdi/
Terms
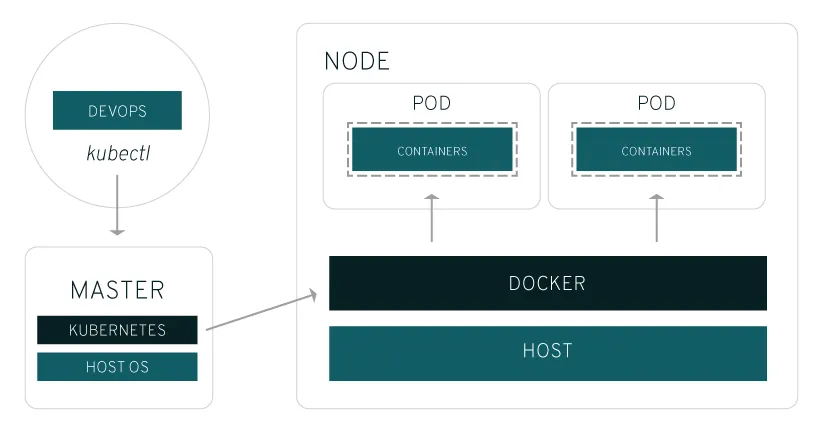
- Node
A node is the smallest unit of computing hardware in Kubernetes.
- Cluster
The cluster as a whole, instead of worrying about the state of individual nodes.
AKA many node group as a cluster.
- Container
Just like Docker, a container references to a image.
- Pod
References to container, a Pod will contain various container like a pool. Also, a Node will contain multiples pods.
- AKA
Containers < Pod < Node < Cluster
- Namespace
Different development stages / area, e.g. dev, staging, production …
Flag is -n
Commands
- View cluster info
CLI
# Check verion
kubectl version
# Check cluster
kubectl cluster-info
# Check pods
kubectl get pods
kubectl describe pods
# Check nodes
kubectl get nodes
# Check deployments status
kubectl get deployments- Create a dummy samples
CLI
# kubectl create deployment <name> --image=<image_path>
kubectl create deployment kubernetes-bootcamp --image=gcr.io/google-samples/kubernetes-bootcamp:v1- Open proxy
You need to open a second terminal window to run the proxy, for external connect.
CLI
kubectl proxy- Get pod name
CLI
kubectl get pods
# NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
# kubernetes-bootcamp-f95c5b745-8zzfm 1/1 Running 0 21m
# The pod name is `kubernetes-bootcamp-f95c5b745-8zzfm`
# Using this can register the name to environment
export POD_NAME="$(kubectl get pods -o go-template --template '{{range .items}}{{.metadata.name}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}')"- Go it pot
CLI
# Print env
kubectl exec "$POD_NAME" -- env
# Inside pod
kubectl exec -ti $POD_NAME -- bash- Expose Your App (Create services)
We have to create a Service to expose the apps.
CLI
kubectl get pods
kubectl get services
# Create services
# kubectl expose deployment/<name> --type="NodePort" --port 8080
kubectl expose deployment/kubernetes-bootcamp --type="NodePort" --port 8080
kubectl get services
kubectl describe services/kubernetes-bootcamp
# In windows 10, you have to port forward the service to minikube
minikube service list
minikube service --url kubernetes-bootcamp
# If it's on other namespace
# minikube service <name> -n <namespace_name>
minikube service --url ingress-nginx-controller -n ingress-nginx- Expose Your App (Pod open)
Testing a pod
CLI
# kubectl port-forward <pod_name> <Out_port>:<Inside_port>
kubectl port-forward nginx-pod 4000:80
# For delete
kubectl delete pod <name>
kubectl delete pod nginx-pod- Rename Pod labels (inside variables)
CLI
kubectl describe deployment
# Print regarding info
kubectl get pods -l app=kubernetes-bootcamp
kubectl get services -l app=kubernetes-bootcamp
# Get name
export POD_NAME="$(kubectl get pods -o go-template --template '{{range .items}}{{.metadata.name}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}')"
echo "Name of the Pod: $POD_NAME"
# Set labels, set the "version" variables to "v1"
kubectl label pods "$POD_NAME" version=v1
# Print regarding info
kubectl describe pods "$POD_NAME"
kubectl get pods -l version=v1- Deleting service
CLI
# kubectl delete service -l app=<name>
kubectl delete service -l app=kubernetes-bootcamp- Deleting ingress
CLI
kubectl get ns
# kubectl delete all --all -n <name>
kubectl delete all --all -n ingress-nginx- Scaling a Deployment
CLI
# Print regarding info
kubectl get deployments
# Get ReplicaSet
kubectl get rs
# Scale deployments
# kubectl scale deployments/<name> --replicas=<number>
kubectl scale deployments/kubernetes-bootcamp --replicas=4
# AKA replicas means the pod numbers to be desire
# View pods
kubectl get pods -o wide
kubectl describe deployments/kubernetes-bootcamp- Endpoints
CLI
# Print regarding info
kubectl get endpoints
kubectl get pod -o wide- Delete all stuff
CLI
kubectl delete deployment,service --all- Create Ingress
CLI
minikube addons enable ingress
kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
kubectl get ingress Last updated on
